How to build Fusion nuclear reactor
Nuclear reactor Dr Tony Miller coursework
Nuclear reactor Dr Tony Miller coursework diagram
- Dounreay white cylindrical dome stood the test of time, white built to reflect sunlight and keep the reactor cool inside.
- Blockwork concrete needed for solid base nuclear reactor and steel frames not timber. Steel frames in reactor core and aluminum can rust.
- Nuclear power plant construction involves numerous welds to connect both components of structures and components of pressurized systems.
- It also involves weld cladding which refers to one metal being deposited onto the surface of another to improve its performance characteristics.
- Fire extinguishers with water and carbon dioxide ideal for high heat situations.
- Fire doors that close automatically like in Royal Cornhill hospital with alarms in every corridor.
- Sodium fast reactor versus best safety molten salt reactor. Molten salt for fission.
- Modular building 3D volumetric construction important to isolate fires in high heat systems.
- A sodium cooled fast reactor is a fast neutron reactor cooled by liquid sodium so North Sea salt water.
- The Sodium Fast Reactor uses liquid sodium as the reactor coolant allowing high power density with low coolant volume fraction and operation at low pressure. While the oxygen free environment prevents corrosion sodium reacts chemically with air and water and requires sealed coolant system.
- assemble vacuum chamber to remove air and pressure. High heat transfer in nuclear reactors so sunction important to remove dust
- Prepare high vacuum pump, valves seal pump and control intense pressure and heat energy.
- Gas transfer pumps and entrapment and capture pumps. Entrapment and capture pumps tend to be used with carbon capture and storage. Pumps which capture gas molecules on surfaces within the vacuum system are unsurprisingly known as carbon or entrapment pumps. These pumps operate at lower flow rates than vacuum pumps such as transfer pumps, however they can provide extremely high vacuum, down to 10-12Torr.
- How do entrapment capture pumps work - when ultra high vacuums are required, entrapment pumps, also known as capture pumps are the most effective choice. They use chemical reactions and cold temperatures rather than moving parts to displace as many gas particles as possible from the sealed chamber.
- How do getter pumps work - pumping relies on the sputtering of getter materials inside a series of cells and by the implantation or burial of the ions produced. The gas molecules pumped by chemisorption (gettererd) and physisorption (ions) are now permanently bound and not able to contribute to the pressure inside the chamber.
- What is a capture pump? Capture pumps operate by capturing the gas molecules on surfaces within the vacuum system. Capture pumps operate at lower flow rates than transfer pumps but can provide ultra-high vacuum down to 10 Torr, and generate an oil free vacuum.
- What is gas transfer pump? Fuel transfer pumps are pumps used in the transfer of fuels and oils. Due to the wide defintion, such pumps can be broken down depending on use and type.
- What is the difference between a transfer pump and a pressure pump? Generally speaking, transfer pumps will have lower PSI capacity but can move larger volumes of water (higher flow rates), whereas High Pressure Fire Fighting Pumps for example will have a higher PSI but move lower water flow rate volumes on a litres per minute measure.
- Can transfer pumps run continuously? As long as the liquid transfer pump does not run out of material, this process is fine. As soon as the pump runs out of material, it will cavitate from loss of fluid trying to pump air and most often run wild until the operator shuts down. The negative effects are numerous on the entire system.
- Does fuel pump PSI matter? It is important to know what the max pressure your engine will require because fuel pressure has a large effect on how much flow a pump can produce. A Fuel pump will flow at its highest volume when there is no pressure (free flow). As fuel pressure increases, fuel flow decreases.
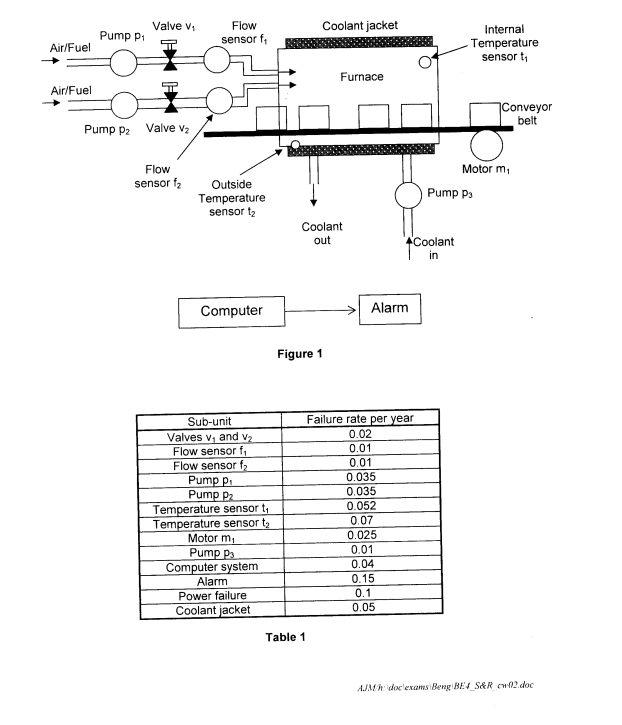
- Ventilation notes from Dr Tony Miller - The product is a plastic moulding used in the construction of ventilation systems. The furnace is used to harden the plastic at a set temperature. The product enters the furnace on a conveyor belt driven by a continuously operating motor, and passes through at a fixed rate. The time the material spends at the elevated temperature is just as important to the success of the operation as the temperature itself. To fire the furnace, pumps spray a mixture of oxygen and fuel into the chamber, at a rate controlled by the valves. Two lines are provided to give some redundancy in case of failure. Only one line is needed for successful operation. The temperature must be kept between upper and lower levels for the chemical process to work properly, and this is governed by controlling the amount of fuel injected. The outside of the furnace is kept cool by a water jacket to prevent injury and structural failure. If, due to some fault in the process, the temperature of the furnace becomes too high the material can catch fire, producing highly toxic gases with serious consequences for personnel and equipment.
- Control systems notes from Dr Tony Miller - Motorised valves control the air fuel supply pipes. A flow meter on each pipe senses the level of the flow. A Computer system performs the function of master controller reading all sensors and transmitting signals to control the valves. On the furnace itself, there are temperature sensors inside and outside the furnace. Water is pumped through the cooling jacket at a fixed rate.
- Computer system notes from Dr Tony Miller - the computer system is at the heart of the process, reading all sensors, activating valves and generating an alarm signal to warn personnel of any danger.
- The computer system and thermometers are the components most prone to failure.
- Build the inner grid of tubes and cables
- Assemble the deuterium system which is a propulsion system to flush out contaminated water important to open needle valve to deuterium tank.
- Turn on high voltage
- Turn on neutron detection and neutrons unstable atoms cause explosions
- Coolant also moderator cools down reactor core